Known for their exceptional strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, these polyethylene plastic sheets are widely used across various industries, from construction and agriculture to packaging, food contact applications, and food service.
This comprehensive guide will explore the key properties, different types, cutting methods, and practical applications of polyethylene plastic sheets, helping you make an informed purchase decision, understand how to best utilize these materials for your projects, and navigate ordering from stock or custom rolls.
What Is Polyethylene Plastic Sheet?
A polyethylene plastic sheet is a highly versatile thermoplastic material made from polyethylene (PE), a polymer renowned for its excellent durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
These sheets are available in various types, including Low Density Polyethylene, High Density Polyethylene, and Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, each offering unique properties tailored to different applications.
Their adaptability, affordability, and availability in various sizes and thicknesses have made polyethylene sheets a staple material across numerous industries, including agriculture, automotive, furniture manufacturing, and even acrylic and plexiglass alternatives for certain uses.

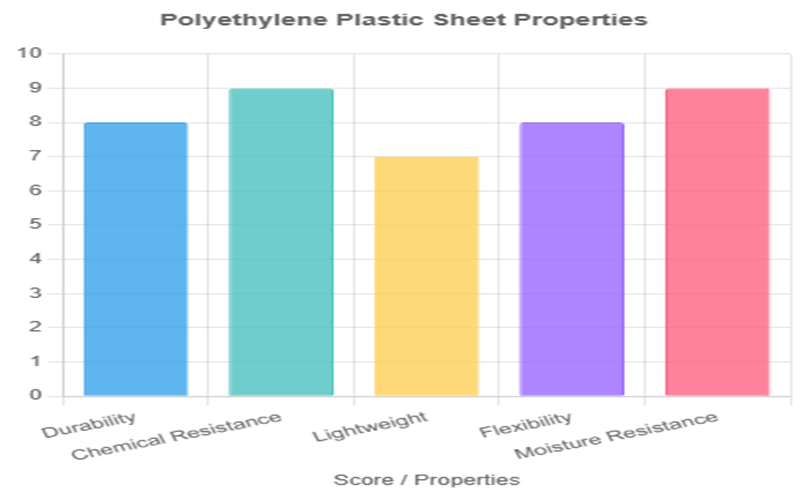
Key Properties Of Polyethylene Plastic Sheet
Polyethylene plastic sheets are valued for their robust and versatile properties, making them a preferred material across numerous applications.
Durability
Polyethylene sheets exhibit excellent impact resistance and tensile strength, allowing them to withstand mechanical stress and wear in demanding environments like industrial liners and conveyor systems.
Chemical Resistance
These sheets offer strong tolerance to acids, bases, and solvents, making them ideal for use in chemical storage, tank linings, and environments where exposure to corrosive substances is common.
Lightweight Nature
Significantly lighter than materials like glass or metal, polyethylene sheets facilitate easy handling, transportation, and installation, reducing labor costs and enabling use in applications like packaging and construction.
Flexibility
Varying rigidity across types—LDPE being soft and flexible, HDPE moderately rigid, and UHMWPE highly durable—allows polyethylene sheets to cater to diverse needs, from flexible films to rigid structural components.
Moisture Resistance
With excellent impermeability, polyethylene sheets resist water absorption, making them suitable for wet environments such as agricultural liners, marine applications, and outdoor storage solutions.
Types Of Polyethylene Plastic Sheets
Polyethylene plastic sheets are available in several distinct types, each tailored to specific applications due to their unique properties.
Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) Sheet
Known for its flexibility, softness, and lightweight nature, LDPE sheets offer excellent chemical resistance and moisture barrier properties.
These qualities make LDPE ideal for applications such as packaging films, plastic bags, and flexible liners in agriculture and food industries where food contact safety is critical.
Additionally, LDPE sheets provide good vapor barrier performance, enhancing their suitability for protective coverings and insulation purposes where moisture control is critical.
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Sheet
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) sheets are known for their superior rigidity, strength, and durability compared to Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE).
These sheets provide excellent impact resistance, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties, making them ideal for a wide range of applications including construction barriers, cutting boards, industrial containers, and outdoor equipment.
HDPE sheets are available in various thicknesses measured in mils or inches, and come in different colors such as natural, black, white, and clear to suit specific project needs.
Their versatility allows for easy cutting, shaping, and fabrication using standard tools, ensuring they can be tailored precisely for different industries like agriculture, packaging, and manufacturing.
Additionally, HDPE’s lightweight nature combined with its robustness makes it a cost-effective and reliable material choice for long-term use in harsh environments.
Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) Sheet
Characterized by exceptional toughness, outstanding abrasion resistance, and excellent impact strength, UHMWPE sheets are widely used in high-wear and demanding applications such as conveyor liners, medical prosthetics, heavy-duty industrial components, and marine equipment.
Their low coefficient of friction and resistance to chemicals make them ideal for environments where durability and longevity are critical.
UHMWPE sheets are available in various sizes and thicknesses, providing versatile options to meet specific project requirements.
| Property/Application | LDPE Sheet | HDPE Sheet | UHMWPE Sheet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High | Moderate | Low |
| Strength | Moderate | High | Exceptional |
| Abrasion Resistance | Low | Moderate | Outstanding |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
| Fabrication | Easy | Easy | Moderate |
| Typical Use Environments | Agriculture, food industry | Construction, manufacturing, outdoor | High-wear, industrial, marine |
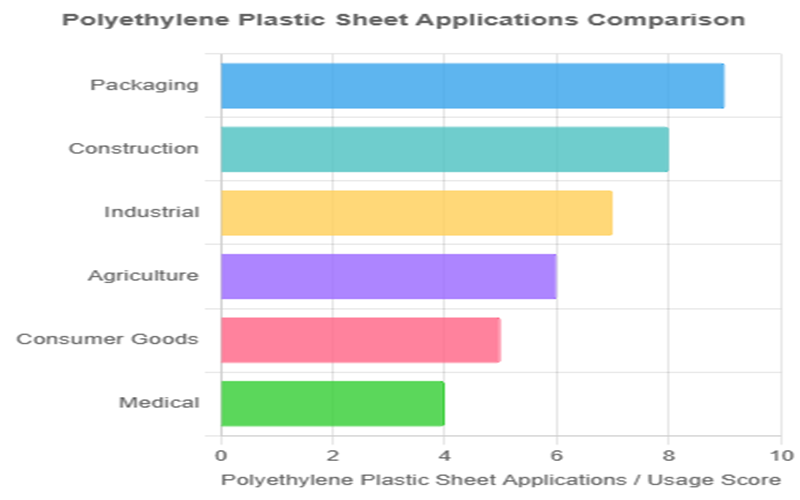
Applications Of Polyethylene Plastic Sheet
Polyethylene plastic sheets are employed across a wide range of industries due to their durability, chemical resistance, and versatility.
Packaging
Polyethylene sheets, particularly LDPE, are widely used for food-grade films, containers, and bags, providing flexible, moisture-resistant, and durable solutions for preserving and transporting food and other products.
Their excellent vapor barrier properties help maintain product freshness and extend shelf life, making them a preferred choice in the packaging industry.
Available in various thicknesses and sizes, polyethylene plastic sheets can be easily cut and shaped to fit different packaging needs, offering cost-effective and reliable performance.
Industrial
Polyethylene plastic sheets are widely utilized as liners for tanks, chutes, and conveyor systems, leveraging their excellent abrasion resistance and low friction properties to enhance efficiency and durability in heavy-duty industrial environments.
Their chemical resistance and impact strength make them ideal for demanding applications where long-lasting performance is critical.
Medical
Polyethylene sheets are widely used in sterile packaging and prosthetic components, thanks to their excellent chemical inertness and ability to meet stringent hygiene and FDA standards required in medical applications.
Their durability and resistance to moisture and chemicals make them ideal for maintaining sterility and ensuring safety in healthcare environments.
Agriculture
Polyethylene sheets, especially LDPE, are widely used in agriculture for applications such as greenhouse covers, irrigation liners, and mulch films.
These sheets provide excellent moisture control, UV resistance, and durability, helping to enhance crop growth, protect soil quality, and improve overall farm productivity.
Their flexibility and weather resistance make them ideal for various outdoor applications, ensuring long-lasting performance throughout the growing season and in other external environments.
Polyethylene Sheet vs Polycarbonate Sheet
When comparing polyethylene sheets to polycarbonate sheets, it’s important to understand their distinct characteristics and ideal uses.
Polyethylene sheets, including types like HDPE and LDPE, are prized for their excellent chemical resistance, moisture barrier capabilities, and flexibility.
They are cost-effective materials commonly used in packaging, agricultural liners, and protective barriers.
However, polyethylene sheets generally have lower impact strength and heat resistance compared to polycarbonate.
On the other hand, polycarbonate sheets are known for their outstanding strength, impact resistance, and optical clarity, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and transparency, such as safety windows, signage, and electronic housings.
While polycarbonate is more expensive, its ability to withstand extreme conditions and provide clear visibility makes it the preferred choice for demanding projects.
Choosing between polyethylene and polycarbonate sheets depends on your project requirements, including factors like budget, environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and whether transparency is necessary.
Understanding these differences will help you select the right material that balances performance, cost, and application needs.

Choosing The Right Polyethylene Plastic Sheet For Your Project
Choosing the right polyethylene plastic sheet for your project involves evaluating key factors to match the material’s properties with your specific needs.
Consider the type of polyethylene—LDPE for flexible applications like packaging films, HDPE for rigid uses such as cutting boards or construction barriers, or UHMWPE for high-wear applications like conveyor liners.
Assess the required thickness and size, as sheets vary from thin films to thick panels, impacting strength and cost.
Chemical and moisture resistance are critical for environments like agriculture or industrial settings, while UV resistance is essential for outdoor use.
Budget constraints and ease of fabrication, such as cutting or thermoforming, should also guide your choice. By aligning these factors with your project’s demands, you can select the most suitable polyethylene sheet for optimal performance.
When ordering, consider checking the stock availability and prices on the supplier’s website. Some suppliers offer sheets in rolls or pre-cut pieces, so note your requirement clearly.

Summary
Polyethylene plastic sheets are a versatile and essential material in many industries. Their durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture and chemicals make them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Whether you need high-density polyethylene (HDPE) for heavy-duty uses or low-density polyethylene (LDPE) for flexible and transparent applications, there is a polyethylene sheet to meet your needs.
In conclusion, understanding the properties and types of polyethylene sheets enables you to make informed decisions for your projects.
These sheets offer numerous benefits and can be customized to fit specific applications. Embrace the potential of polyethylene plastic sheets and elevate your projects to new heights.

Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Main Types Of Polyethylene Plastic Sheets?
The main types of polyethylene plastic sheets are high-density polyethylene (HDPE), low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMW).
How Can I Cut Polyethylene Plastic Sheets?
You can cut polyethylene plastic sheets effectively by using a utility knife and ruler for thinner sheets, while thicker sheets are best handled with power tools such as a table saw equipped with blades designed specifically for plastic.
What Are Common Applications Of Polyethylene Sheets?
Common applications of polyethylene sheets include construction, agriculture, packaging, food contact, painting, and food service, owing to their durability and versatility.
How Effective Are Polyethylene Plastic Sheets As A Moisture Barrier In Applications?
Polyethylene plastic sheets are highly effective as moisture barriers in construction, providing excellent impermeability to water and vapor. Depending on the specific use, they can serve as vapor barriers, protective sheeting, or geomembranes, helping to protect structures from moisture damage.
What Factors Should I Consider When Choosing A Polyethylene Sheet?
When choosing a polyethylene sheet, consider the application, thickness, type of polyethylene, supplier certifications, prices, and the cost-performance trade-offs. Additionally, check the supplier’s website for stock availability, shop options, and cart functionality to ensure a smooth purchase process.





