Whether you’re involved in construction, packaging, or creative applications, choosing the right plastic sheet thickness is a fundamental requirement for ensuring product quality and safety.
The thickness of a plastic sheet directly affects its strength, flexibility, durability, and cost, making it a critical factor in meeting your specific needs.
With a wide variety of materials and thicknesses available, understanding how to select the optimal plastic sheet thickness can save time, reduce costs, and enhance performance.
This guide will walk you through the essential considerations to help you make an informed decision tailored to your project’s requirements.
Definition Of Plastic Sheet Thickness and Measurement Units
Plastic sheet thickness refers to the measurement of a plastic sheet’s cross-sectional depth, which significantly influences its performance characteristics, such as strength, flexibility, and weight.
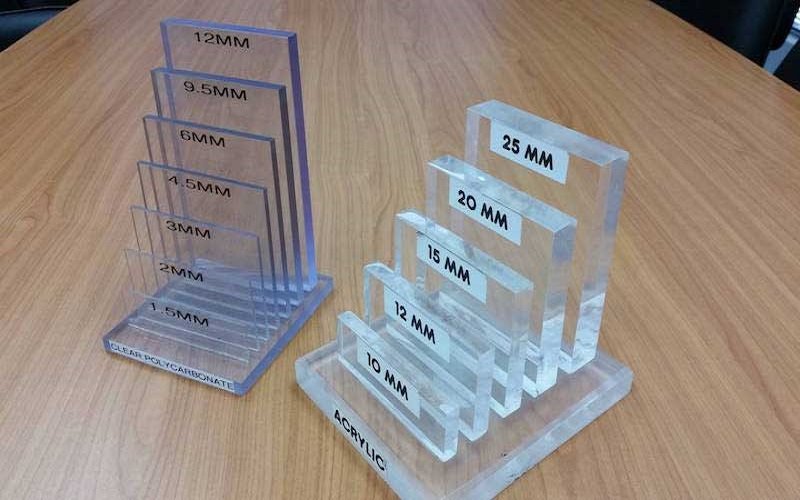
Plastic sheet thickness is typically measured in millimeters (mm) or mils (also known as mil thickness, where 1 mil = 0.001 inches or 0.0254 mm), depending on the region or industry.
For example, thinner sheets (e.g., 0.5–2 mm) are often used for flexible applications like packaging, while thicker sheets (e.g., 5–25 mm) are suited for structural purposes.
Understanding the measurement unit is critical when selecting a sheet, as specifications may vary across suppliers or regions.
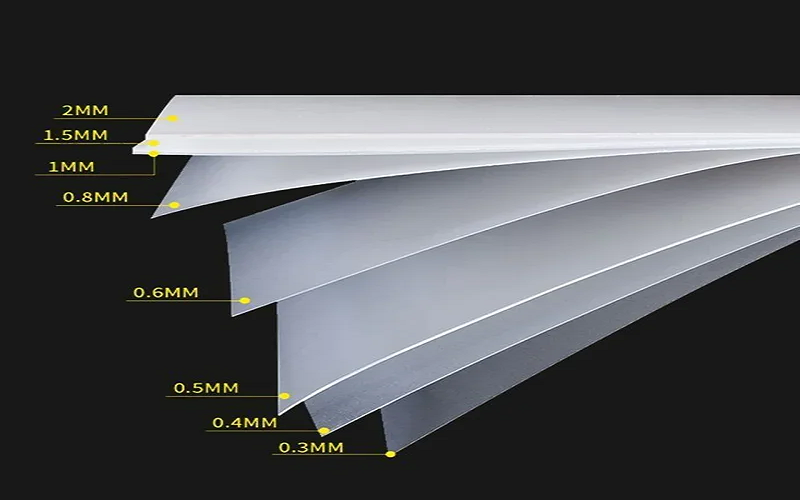
Thickness Range Of Plastic Sheets
Plastic sheets come in a wide range of thicknesses to suit various applications, typically categorized as follows:
Thin Sheets (0.03–2 mm)
These sheets are flexible and lightweight, commonly used for packaging films, protective covers against dust, and applications where ease of forming and cutting is important. Thin sheets are often expressed in microns and are ideal for projects requiring clear, easily handled plastic film.

Medium Sheets (2–6 mm)
Offering a balance between flexibility and rigidity, medium thickness sheets are suitable for furniture components, display cases, and construction enclosures. They provide enhanced durability while still being manageable for laser cutting and shaping.
Thick Sheets (6–25 mm or more)
Thicker sheets provide maximum strength and rigidity, making them ideal for load-bearing applications, outdoor covers, and heavy-duty projects. These sheets resist wear, wind, and heat, and are commonly reinforced with string reinforcement for added tear resistance.
Selecting the right thickness depends on your project’s specific needs, including the required strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
No matter the size or form of your application, understanding these thickness ranges will help you choose the most suitable plastic sheeting to ensure durability and performance.
Factors Determining Sheet Thickness
The thickness of plastic sheeting is determined by various factors that collectively influence its performance and suitability for specific applications.
These factors include the material’s composition, the presence of additives, and the intended use or job requirements.
Thicker sheets are generally stronger, more rigid, and more durable, making them ideal for load-bearing applications, outdoor covers, and situations where resistance to wind, wear, and cracking is critical.
Conversely, thinner sheets offer greater flexibility and are easier to handle and shape, making them suitable for tasks where weight, ease of installation, and cost balance matter.
String reinforcement is a common method to enhance the strength and tear resistance of plastic sheeting without significantly increasing the mil thickness.
This reinforcement improves durability, especially in demanding environments such as construction enclosures or greenhouse covers.
Additionally, the type of plastic material—such as polyethylene, PVC, or reinforced plastic sheeting—affects the required sheet thickness to achieve the desired balance of rigidity, flexibility, and durability.
Manufacturers often provide a gauge or thickness chart to help match the sheet thickness to specific project needs.
Understanding these factors will help you select the right plastic sheet thickness, no matter the thickness range or application, ensuring your project meets both performance and budget requirements.
Common Uses For Different Thickness Of Plastic Sheeting
The thickness of plastic sheeting determines its suitability for various applications, as it affects strength, flexibility, weight, and cost.
Below is an overview of common uses for different thickness ranges, categorized by material and application, to help guide your selection.
Construction Enclosures
Plastic sheeting is widely used in construction and industrial settings for its durability, versatility, and resistance to environmental factors.
Recommended thicknesses vary based on the structural requirements and material chosen.
| Application | Materials | Recommended Thickness | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Panels | PVC, Polycarbonate, HDPE | 6–12 mm | Wall partitions, cladding, load-bearing panels |
| Roofing | Polycarbonate, Acrylic | 4–10 mm | Skylights, canopies, greenhouse roofing |
| Insulation | HDPE, PVC foam boards | 10–20 mm | Thermal or sound insulation in walls, floors, HVAC |
Packaging
Plastic sheeting in packaging applications prioritizes flexibility, lightweight design, and protection. Thickness selection depends on the level of protection needed and the material’s properties.
| Application | Materials | Recommended Thickness | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective Packaging | Polyethylene (LDPE/HDPE), Polypropylene | 0.03–0.5 mm (films), 0.5–2 mm (sheets) | Food packaging, shrink wrap, product wrapping for shipping |
| Containers | PVC, PET, Polystyrene | 0.5–2 mm | Blister packs, clamshell packaging, rigid containers for retail |
Creative and DIY Projects
Creative and DIY applications prioritize aesthetics, workability, and versatility. Thicknesses are chosen based on the project’s structural and visual requirements.
| Application | Materials | Recommended Thickness | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Art Installations | Acrylic, Polycarbonate | 2–6 mm | Sculptures, light diffusers, decorative panels |
| Displays | Acrylic, PVC | 2–5 mm | Retail signage, exhibition stands, point-of-purchase displays |
| Models and Prototypes | ABS, Polystyrene, PVC | 1–3 mm | Architectural models, product prototypes, hobbyist crafts |
Specialized Uses
Specialized applications, such as medical, automotive, or marine uses, require tailored thicknesses to meet stringent performance standards.
| Application | Materials | Recommended Thickness | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Applications | Polycarbonate, PETG | 1–6 mm | Protective shields for medical equipment, sterile packaging, face shields |
| Automotive Applications | Polycarbonate, ABS | 3–10 mm | Interior panels, headlight covers, dashboard components |
| Marine Applications | HDPE, Polycarbonate | 6–25 mm | Boat windshields, hatch covers, decking components |
Practical Tips For Choosing The Right Thickness
When selecting the right plastic sheet thickness for your project, consider the following practical tips to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness:
- Assess the Application Requirements
Determine the primary function of the plastic sheet. For load-bearing applications or outdoor covers, thicker sheets with higher durability and rigidity are essential. For flexible packaging or dust covers, thinner sheets may suffice. - Consider Environmental Factors
Exposure to elements such as wind, heat, and UV radiation can affect the longevity of plastic sheeting. Choosing a thickness that accommodates these factors, possibly with added UV stabilization or string reinforcement, will enhance durability. - Balance Flexibility and Strength
Thicker sheets offer strength and rigidity but may be harder to shape or cut. Thinner sheets provide flexibility and ease of handling but may lack durability. Select a thickness that balances these needs based on your project’s demands. - Use Manufacturer’s Thickness Charts
Refer to thickness charts provided by manufacturers to match the sheet thickness with your specific application. These charts often include recommendations based on material type and intended use. - Factor in Budget and Material Costs
Thicker plastic sheets generally cost more. Evaluate your budget constraints alongside performance requirements to choose the right thickness without overspending. - Test Samples When Possible
If uncertain, request samples of various thicknesses to test for strength, flexibility, and suitability for your project before making a bulk purchase.
By carefully considering these factors and understanding the role of plastic sheet thickness, you can select the right material that meets your project’s needs efficiently and economically.