Acrylic sheet and Plexiglass are widely used materials known for their clarity, durability, and versatility, often serving as lightweight alternatives to glass in various applications.
Despite their similarities, confusion persists about whether these terms refer to the same material or distinct products with unique properties.
Terms like ‘Plexiglas’ are examples of trade names and generic trademarks, and various brand names—such as Plexiglas®, Lucite®, Acrylite®, and Perspex®—are often used interchangeably, which contributes to the confusion between proprietary trade names and the generic term for acrylic sheets.
This article aims to clarify the relationship between acrylic sheet vs plexiglass by comparing their composition, properties, and uses, empowering readers to make informed decisions when selecting the right material for their projects.
Definitions Of Acrylic Sheets And Plexiglass
Acrylic sheets, chemically known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), are transparent thermoplastics that boast glass-like clarity and impressive durability. These sheets are produced either through extrusion or cell casting and come in a variety of forms such as clear acrylic, colored, frosted, or impact-resistant options.
They are manufactured by various brands, including Acrylite, Optix, Perspex, Lucite, and other PMMA products. Lucite is a well-known trademarked brand for high-quality cast acrylic sheets, similar to Plexiglas. There are many other brands producing high-quality acrylic sheets as well.
These versatile materials are widely used across industries ranging from construction to signage and furniture due to their lightweight, easily shaped nature and broad range of applications, including custom sizes.
Plexiglas (with one ‘s’) is the original brand name and a registered trademark of clear cast acrylic sheets introduced by Rohm and Haas in 1933, initially developed as a shatter-resistant alternative to glass and gaining prominence during World War II for aircraft canopies.
The term “plexiglass” (with two ‘s’) is often used generically to refer to acrylic sheets made in the same way, though Plexiglas is a specific brand with certain manufacturing qualities.
Over time, plexiglass sheet has evolved to offer enhanced properties such as superior clarity and chemical resistance, maintaining popularity in automotive and protective barrier applications.
While plexiglass is a type of acrylic, it differs from other plastics like polycarbonate, which offers higher impact resistance but lower clarity. These are different types of plastic, and acrylic is often chosen over other materials for its clarity and versatility. The term “plexiglass” and “acrylic” are often used to refer to the same product, leading to confusion, but it specifically refers to a brand known for its quality and manufacturing process.

The Manufacturing Process of Acrylic Sheets
The journey from raw material to finished product for acrylic sheets involves two primary manufacturing processes: extrusion and cell casting. Each method impacts the sheets’ properties and suitability for various applications in acrylic sheet manufacturing. Let’s take a closer look at these processes.
Cell casting begins with assembling glass cells and filling them with a syrupy liquid methyl methacrylate (MMA). The filled cells are then cured under pressure, resulting in high-quality sheets with fewer impurities and superior optical clarity.
The resulting product is known as cast acrylic sheet, which is valued for its excellent optical and mechanical properties. This method is labor-intensive, time-consuming, and costly but yields durable and aesthetically pleasing products.
In contrast, the extrusion process involves continuously forcing heated acrylic polymer through a die, creating sheets with a consistent thickness. Both cast acrylic sheet and extruded acrylic can be molded into various shapes and are easily formed when heated, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
This method produces more affordable and flexible sheets, although they may contain more impurities and have slightly lower optical quality compared to cell-cast sheets. Additionally, cut acrylic sheets can be produced using this method.
Ultimately, the choice between extrusion and cell casting depends on the specific requirements of the project and budget considerations.
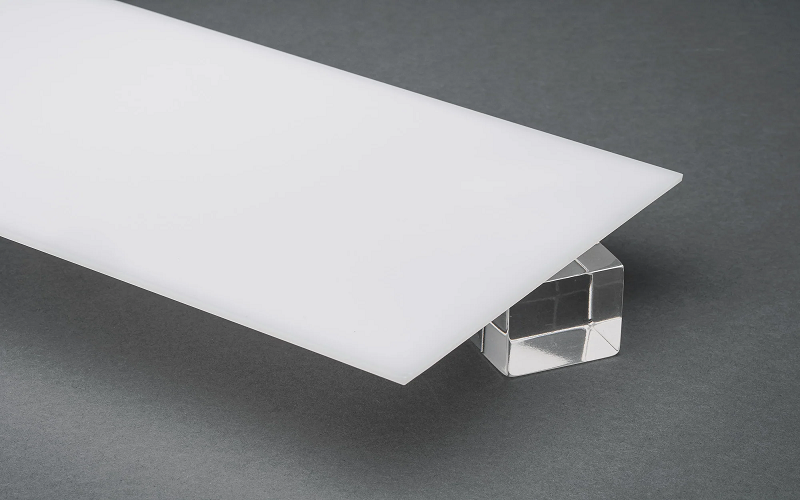
Acrylic Sheet vs Plexiglass: Key Properties Comparison
When comparing acrylic sheets and plexiglass, it’s essential to consider their key properties. These materials share many similarities due to their PMMA composition but differ in specific aspects.
Plexiglass is more rigid than some extruded acrylic sheets, which contributes to its structural strength and durability. In terms of impact resistance, both acrylic and plexiglass are less likely to break than glass.
If they do break, they tend to fracture into dull-edged pieces rather than dangerous shards, making them safer for various applications.
We’ll examine their physical, chemical, and thermal properties to highlight these differences.
Physical Properties
Both acrylic sheets and plexiglass boast impressive transparency and clarity, with light transmittance rates of up to 92%, rivaling that of glass. Acrylic sheets are available in various forms, including transparent, colored, and frosted options, offering flexibility in design.
Acrylic and plexiglass often include anti-glare or scratch-resistant coatings, enhancing their surface performance. Acrylic glass is also a popular choice for many applications, including acrylic plexiglass.
In terms of weight and density, both materials are approximately half the weight of glass, with a density of around 1.19 g/cm³. This lightweight nature makes them easier to handle and install, an advantage in many applications. There is no significant difference between the two in this regard.
When it comes to strength and impact resistance:
- Acrylic sheets outperform glass by being 10-20 times more impact-resistant.
- Acrylic sheets are less durable than polycarbonate and may crack under extreme impact.
- Plexiglass shares similar impact resistance to acrylic but can be enhanced with special formulations to improve toughness or abrasion resistance.
Chemical Properties
Both acrylic sheets and plexiglass exhibit good resistance to diluted acids and alkalis, making them suitable for various chemical environments. However, they are sensitive to solvents such as acetone and alcohol, which can damage the material. While both are suitable for outdoor use, specific plexiglass formulations may offer enhanced resistance to certain chemicals and prolonged exposure.
Acrylic sheets naturally possess some UV resistance, with certain models incorporating UV inhibitors to prevent yellowing and degradation over time. Plexiglass often includes UV-stabilized options, ensuring long-term clarity and performance in outdoor applications.
Thermal Properties
Acrylic sheets and plexiglass share similar thermal properties:
- Softening points range from 160-180°C (320-356°F).
- Not suitable for high-temperature environments.
- Continuous usage temperature should remain below 80°C (176°F).
- Some plexiglass variants might offer slightly improved heat resistance, but the difference is minimal.
Both materials have a thermal expansion coefficient of approximately 0.000075 mm/mm/°C, higher than that of glass. This property necessitates design considerations for environments with significant temperature fluctuations, especially when using the same material.
Common Applications Of Acrylic And Plexiglass Sheet
Acrylic sheets and plexiglass are widely used across various industries due to their high transparency, lightweight nature, and ease of fabrication. These materials are common in construction, advertising, display, and industrial applications, offering versatility to designers and engineers alike.
Acrylic sheets are more commonly used in cost-sensitive, high-volume applications due to their affordability and diverse range of brands and pricing options.
In contrast, plexiglass, with its brand recognition and perceived higher quality, is preferred in high-end or specialized fields such as aviation and automotive industries.
In advertising and furniture production, the variety and lower cost of acrylic sheets make them a popular choice.
Conversely, plexiglass is favored in the aviation and safety sectors due to its reliability and brand reputation, often featuring enhanced properties like scratch resistance or improved impact strength.

Is Plexiglass Cheaper Than Acrylic?
When it comes to cost, acrylic sheets generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to plexiglass. Plexiglass is often seen as higher quality due to its brand recognition. This perception contributes to its elevated price point.
Extruded acrylic sheets are typically more affordable and flexible than cell-cast acrylic sheets, which are more durable but also more expensive. The difference between acrylic options often depends on the project’s specific requirements and budget constraints.
Factors such as size, thickness, and quantity influence the overall cost of acrylic sheets. Understanding these variables helps you estimate project expenses and make cost-effective decisions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Of Acrylic Plexiglass Sheet
Acrylic sheets are a sustainable choice due to several factors:
- They can be recycled multiple times without losing quality, contributing to environmental friendliness and supporting a circular economy.
- Their production requires less energy compared to materials like glass or metal, enhancing their sustainability profile.
- Their lightweight nature results in lower carbon emissions during transportation, making them an eco-friendly option, especially when paired with solar panels.
Acrylic’s inherent UV resistance ensures that it maintains its clarity and strength over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. These long-term environmental benefits make acrylic sheets a durable material choice that is also sustainable.

Maintenance Tips for Acrylic Sheet and Plexiglass
Proper maintenance is key to preserving the clarity and durability of your acrylic sheet and plexiglass products. Regular cleaning and care will help keep these materials looking their best and extend their lifespan.
To clean acrylic and plexiglass sheets, use a mild soap solution and a soft, non-abrasive cloth. Gently wipe the surface to remove dust and fingerprints, avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that can cause scratches or cloudiness. For minor scratches, a specialized acrylic polish can be applied to restore the smooth finish and maintain the sheet’s transparency.
For added protection, consider applying a protective coating or film to your acrylic sheet. This extra layer helps prevent scratches and shields the material from everyday wear and tear. If your acrylic or plexiglass sheet sustains deeper damage, professional repair or replacement may be necessary to restore its appearance and performance.
Avoid using high-pressure washes or rough sponges, as these can damage the surface and reduce the durability of your acrylic and plexiglass materials. By following these simple maintenance tips, you can ensure your sheets remain clear, attractive, and long-lasting.
How To Choose Acrylic Sheet And Plexiglass?
Choosing between acrylic sheet and Plexiglass involves evaluating your project’s specific requirements, as the two materials are fundamentally similar but differ slightly due to brand-specific formulations, quality, and market positioning.
Acrylic sheet and Plexiglass are nearly identical in composition and performance, with Plexiglass offering potential advantages in quality control, specialized grades, and brand trust.
Choose acrylic sheet for cost-effective, versatile applications with flexible options, and opt for Plexiglass when premium performance, certifications, or specific enhancements (e.g., abrasion resistance) are required.
Always review manufacturer specifications and align your choice with the project’s functional, aesthetic, and budgetary needs.
Additionally, consider the fabrication methods involved in your project. For instance, if you plan to cut acrylic sheets into custom sizes or intricate shapes, techniques like laser cutting can provide precise and clean results, minimizing material waste and enhancing the final product’s quality. Both acrylic sheets and Plexiglass respond well to laser cutting, but the specific grade and thickness may affect the ease and quality of the cut.
Environmental factors also play a role in your decision. If the application involves prolonged outdoor exposure, selecting materials with enhanced UV resistance and weatherability—often found in certain Plexiglass formulations—can ensure longer-lasting clarity and durability.
In summary, your choice between acrylic sheet and Plexiglass should be guided by the balance of cost, performance, fabrication needs, and environmental conditions to achieve the best outcome for your specific project.
Summary
In summary, while acrylic sheets and plexiglass share many similarities due to their PMMA composition, they differ in specific aspects such as manufacturing processes, cost, and brand recognition.
Acrylic sheets offer versatility and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Plexiglass, with its enhanced properties and brand reputation, is favored in specialized and high-end industries.
By understanding these differences, you can confidently choose the right material for diy project, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Embrace the clarity and durability of acrylic products and make informed decisions to elevate your designs and constructions.